Top 10 Mobile Usability Testing Methods You Should Know
Almost 90% of the time people spend on their phones is spent on 3 or 4 mobile apps. Hence, it’s reasonable to say that creating an app for your business is a strategic way to ensure people find you easily on the internet and have more satisfying user experiences. However, before you jump right into mobile application development and app management, it’s critical to identify the importance of an app’s usability.
What is Mobile Usability Testing?
Mobile usability testing is simply the process of simulating how an actual user would use an app. It involves testing various factors, including:
- Interface experience,
- Performance quality,
- Functionality,
- Navigation, and more.
An intuitive and pleasant user experience is at the heart of every app. Hence, the app development team and QA testers should always ensure an app delivers its predefined functions to drive higher customer engagement and satisfaction.
Why Run Mobile Usability Testing?
The primary purpose of running mobile usability testing is to identify possible glitches and ensure that it truly delivers the expected value and practicability for users. Usability testing helps to ensure that your app is adding value to your business, as well as meeting the expectations of the final users.
Apart from enhancing user experiences, here’s why it's crucial to run a mobile app usability test before releasing it officially for public download:
- Identify challenges in design
- Discover opportunities to enhance design
- Understand your user behavior and preferences
- Cut down overall troubleshooting expenses and time
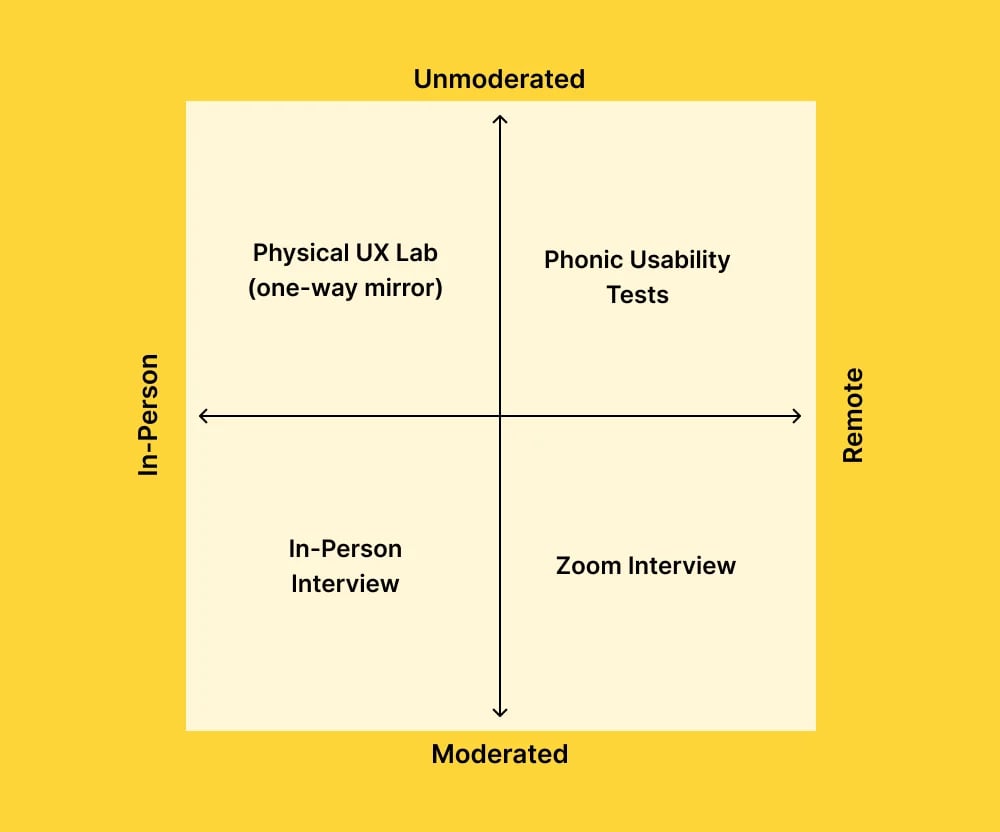
Furthermore, according to research, 67% of users deleted a mobile app after experiencing unclear navigation and insufficient information. If your business offers apps that are used both in-house and customer-facing, usability tests will help you minimize tech errors and improve end-user experiences when you remotely update apps across all company-owned devices.
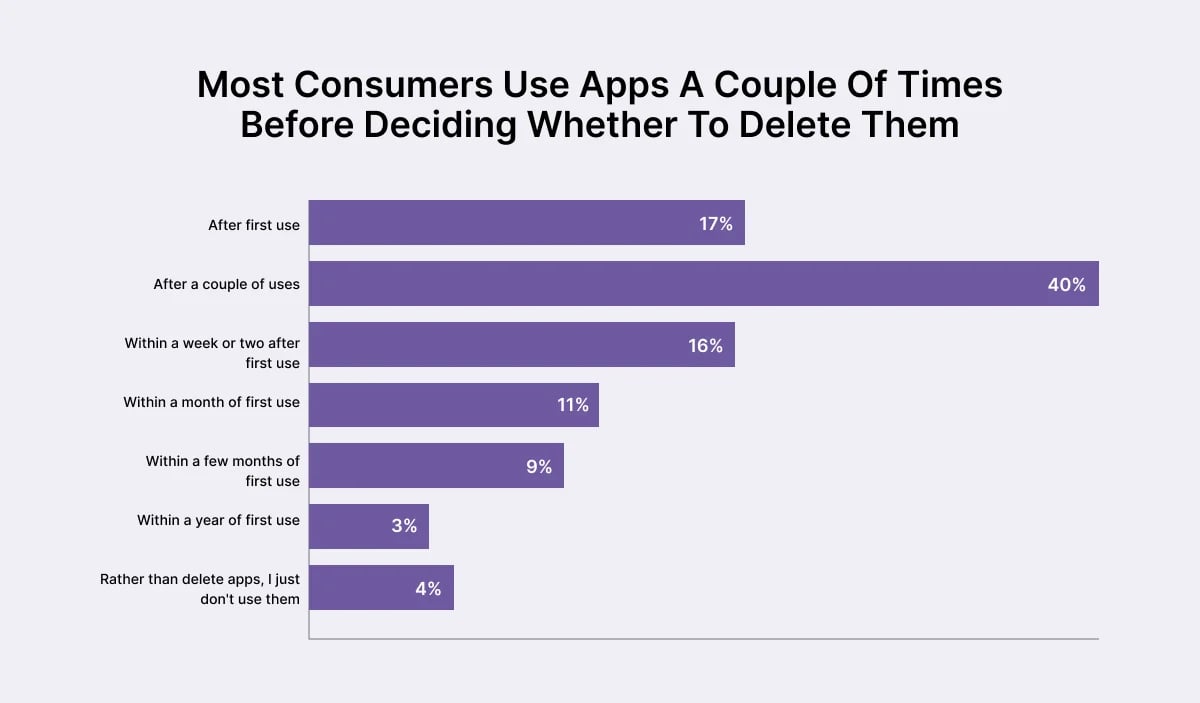
What factors are involved in mobile usability testing?
Seamless collaboration among various elements is essential to conducting effective mobile usability testing. Here's a step-by-step guide to get started:
1. Define clear objectives and tasks: Before initiating variant tests, establish clear objectives and tasks that you aim to accomplish.
2. Prepare test documents: Ensure you have the necessary test documents, such as content forms, pre-and post-test questionnaires, and orientation scripts, ready.
3. Recruit test participants: Find suitable test participants who are willing to perform all requested tasks, ensuring diverse representation if necessary. Participants must:
- Reflect the characteristics of the target audience.
- Possess a mobile device running the operating system compatible with the mobile app's design.
- Be present at the designated time and location for lab-based usability testing.
- Be willing to sign a permission form consenting to participate in the usability test.
4. Choose appropriate testing methods: Depending on the aspects of your mobile usability tests, QA testers should determine which type of mobile testing method is most suitable to get more impartial results.
5. Analyse the data: After the tests, you need to look at the data. The most important thing is to figure out what it means. What should you look at? Here are some things you'll get:
- Written feedback.
- Video recordings.
- Completed/unfinished tasks.
Review each user test session individually. Go over all available resources for each participant, such as notes, transcripts, or any other relevant information.
Identify both positive and negative trends, as well as challenges and obstacles encountered by users. Compare your findings with other information to see if certain devices or types of people had more issues.
Always make a report the same way so you can compare changes over time.
Different types of Usability testing
Before you choose how to test, it's crucial to really know your audience – what they think, believe, feel, and want. To figure out which type of usability testing suits your needs, start by setting your research goals and understanding what you want to achieve.
1. Remote or In-Person Testing
Remote tests are done over the phone or online, while in-person tests have a moderator or researcher present with the tester. Remote tests are usually cheaper and quicker because you don’t need physical space or might not have to pay participants. They also let you test more people with fewer resources. In-person tests provide more data since the observer can see body language and facial expressions. They also allow the observer to understand a participant’s thoughts and motivations better.
2. Moderated or Unmoderated
Moderated tests can be done in-person or remotely and are led by a trained person who knows the test and the app well. They can answer any questions the test-taker might have. Unmoderated tests are unsupervised and can be done in a testing lab or at home. Because there's no one guiding them, participants can't ask questions. Moderated tests usually give more detailed results but can be more expensive.
3. Explorative, Comparative, or Assessment
Explorative tests ask open-ended questions, and participants give their impressions and opinions with little guidance. They're often used early in product development. Comparative tests ask testers to choose between solutions, often for competitive comparisons. Assessments gauge a participant’s satisfaction with app functionality and overall usability.
10 usability testing methods to try out
Now, let’s go over these methodologies more in detail:
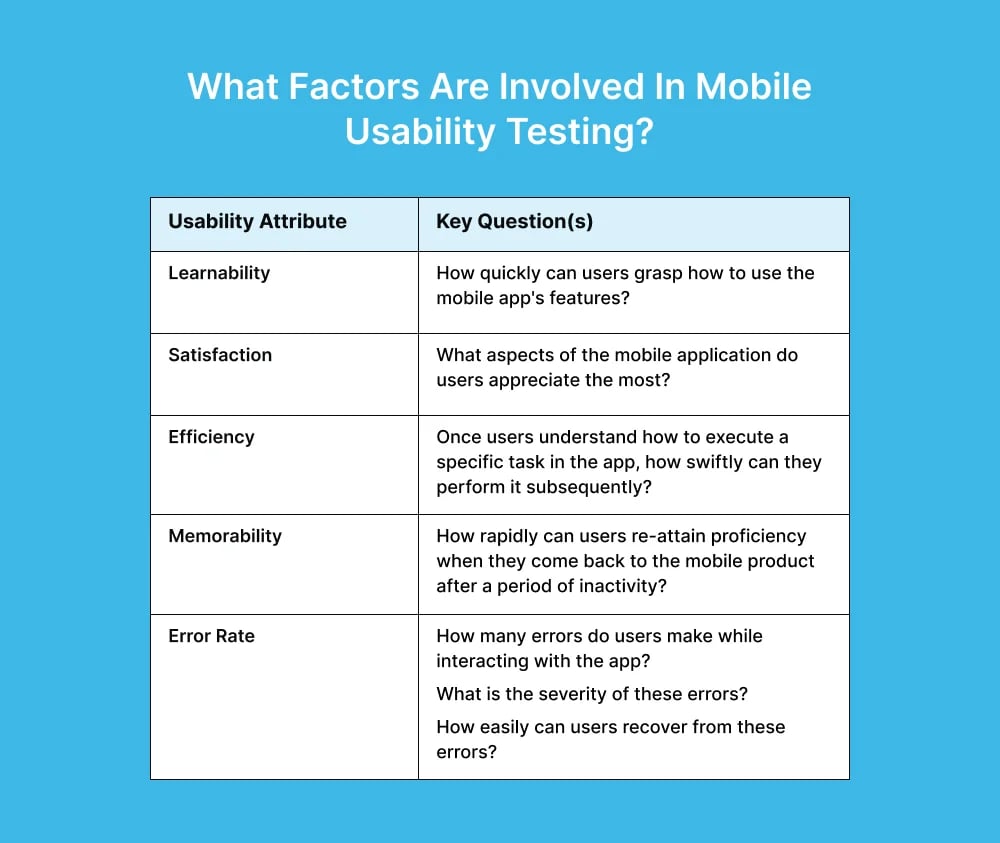
1. Moderated Usability Testing
A moderated testing usually offers more in-depth results since the moderator can ask for more information and follow-up questions. It can be done on-site or remotely. Moderators can also ask participants to elaborate more on a particular response to find out how users feel about an app during different usage processes. You can have better control of the test flow and receive more qualitative feedback.
However, moderated usability testing has drawbacks. On-site testing often consumes a significant amount of time and resources, making it costly for organizations to execute, especially for a small participant pool. However, if you choose remote testing, you may not catch body language.
Therefore, it's advisable to opt for moderated testing when seeking to understand the rationale behind user behavior. Unmoderated usability testing may be a more suitable alternative for uncovering user behavior patterns.
2. Unmoderated Usability Testing
Unlike moderated testing, unmoderated usability testing requires participants to complete all the tasks by themselves, without additional instructions or interference from the moderator. Unmoderated testing is more time-effective and less costly. It is perfect for testing users’ natural context when navigating an app. And it’s most suitable if you want to run large sample studies for more quantitative testing.
Since unmoderated testing requires little, almost no supervision, you’ll need to make sure all the instructions are clearly given prior to the test. The majority of unmoderated testing is completed remotely, making a stable internet connection a top priority for the test participants’ environment. As a general rule of thumb, it’s recommended to use unmoderated usability testing to observe and measure unbiased user patterns.
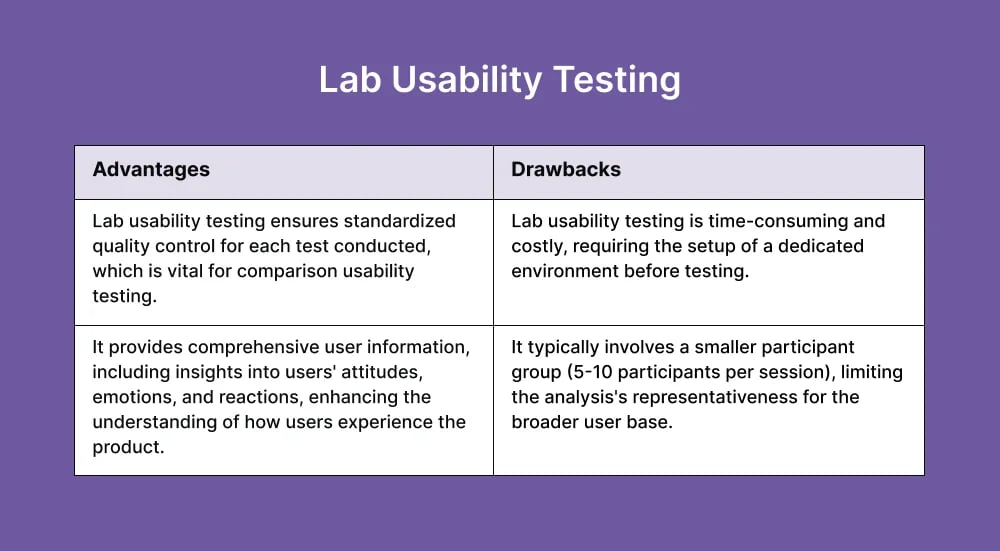
3. Lab Usability Testing
Lab usability test asks participants to complete specific tasks instructed by a trained moderator within a purposely designed laboratory. There are two rooms divided by a one-way mirrored window to allow note-takers to observe the test without being seen by participants and affect the results. The moderator will ask questions, give instructions, and reply to feedback in real time, similar to moderated testing mentioned earlier. You may also record the session for further review and analysis afterward.
4. Guerilla usability testing
For guerilla usability testing, participants are usually chosen randomly from a public place, like a coffee shop, mall, airport, or supermarket, and asked to perform a short usability test in exchange for small rewards such as gift cards or coupons.
Guerrilla testing is often conducted on a wide range of people who have no previous experience with a product.
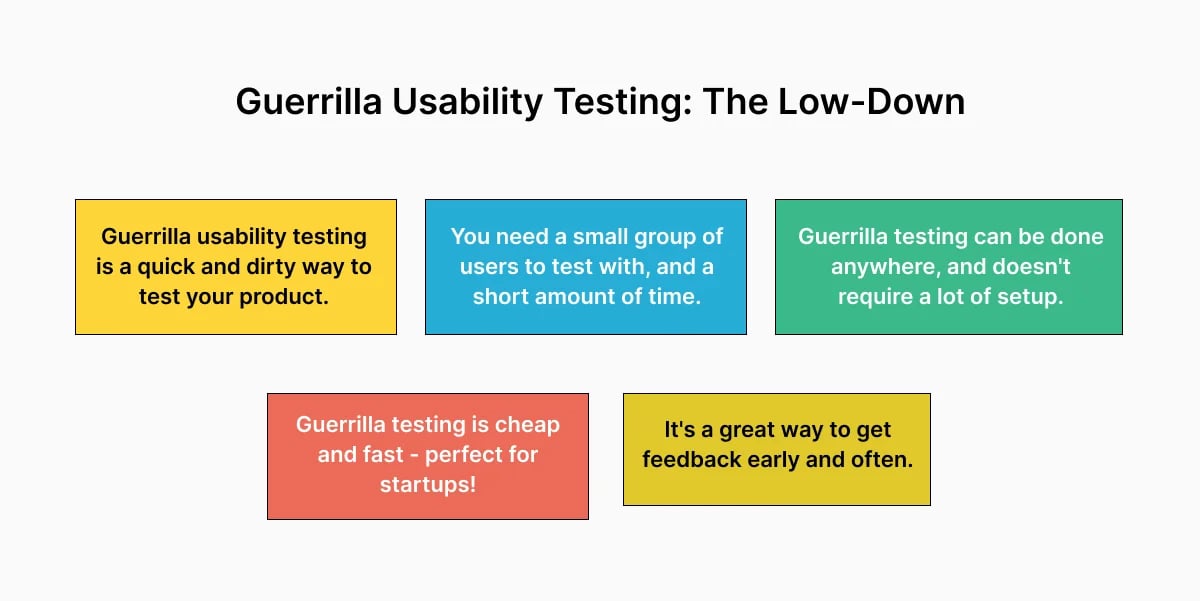
Guerrilla testing sometimes serves as an ad hoc test for the UI/UX team to understand the functionality and design. It also gives your app more brand exposure before it actually hits the market.
Though guerrilla testing is a convenient mobile usability testing option, it’s not ideal for extensive information gathering or follow-up questions because people are usually less patient and willing to spend more than 5-10 minutes with a test.
5. Contextual Inquiry
The contextual inquiry method involves observing how participants interact with the product in their natural environments, such as offices or homes. The researchers then watch how participants complete a task and ask them the reasons behind their actions to gain a deeper understanding of user behavior.
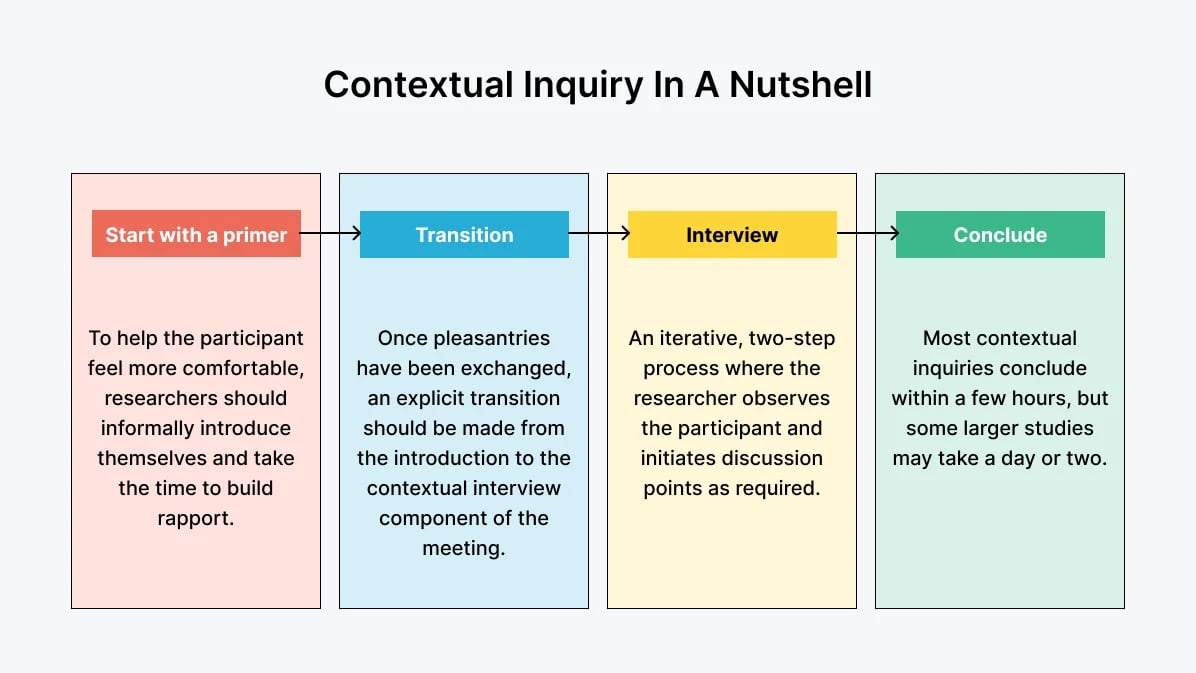
This method is an excellent way to retrieve reliable information about users, including work preferences, personal behavior, and the scenarios needed for the product. These insights are essential at the initial stage of production as you’ll need as much data on personas, feature requests, content, and architecture as possible. Once you release a product, you can also use contextual inquiry to test whether your design actually matches users’ needs.

6. Eye-tracking Test
Eye-tracking tests observe users’ eye movement through a pupil-tracking device. The moderator uses heatmaps and pathway diagrams to analyze how users direct their attention when asked to finish a task.
Areas where a user's gaze pauses are referred to as fixations, often represented by circles. The size of the circle corresponds to the duration of the fixation – larger circles indicate longer fixations.
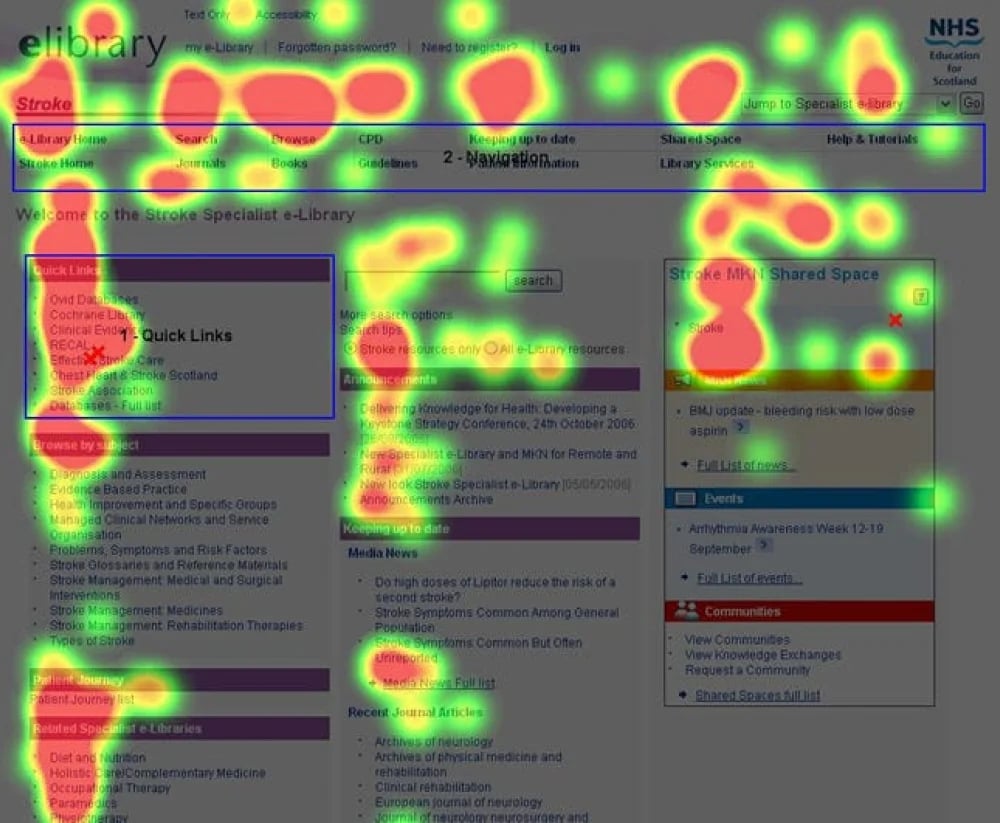
Eye tracking enables you to evaluate the ease and intuitiveness of navigation on your website or app. Insights from eye-tracking studies help address specific research questions, such as identifying distracting elements on the screen.
The downside of eye-tracking tests is the cost of equipment and software required. You will also need to hire trained technicians to help you operate the device. Eye-tracking tests usually involve a smaller group of people. Therefore, the results may not be very objective.
7. Screen Recording Test
Screen recording tests are a method of usability testing that records sessions of how users are using mobile devices to complete specific tasks instructed by a moderator. It clearly identifies the ease and difficulties users experience when navigating a mobile app. With video and audio recording features, moderators can analyze user clicks, swipe movements, and opinions for more insights.
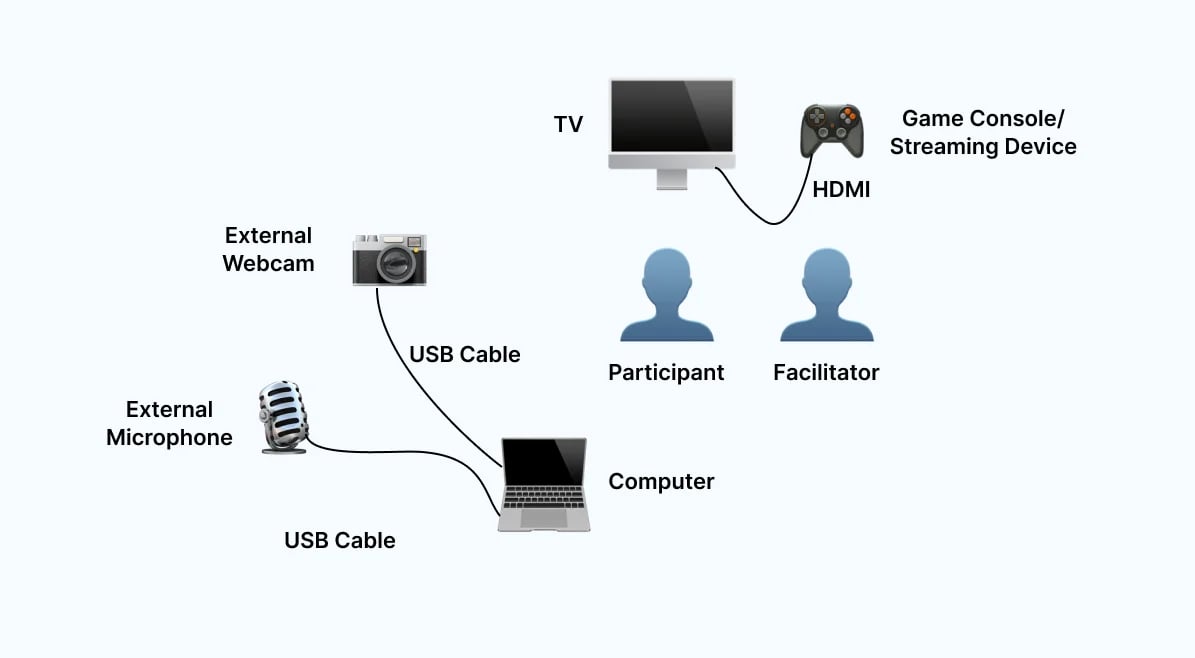
8. Phone Interview
A phone interview is one kind of remote testing. A moderator here records and verbally instructs a participant to complete tasks on their mobile devices and collect feedback. It’s a rather cost-effective way to sample users from different geographic locations, and it’s less expensive than conducting one-on-one personal interviews. This is most recommended if you want to collect a lot of data in a shorter period of time. However, to avoid any bias, there are some questions you shouldn't ask.

9. Card Sorting
Card sorting mobile usability testing helps developers understand whether the product design is intuitive and easy to use by nature. Test participants are asked to sort virtual cards that represent various segments in the app’s navigation to make categorization easier to understand.
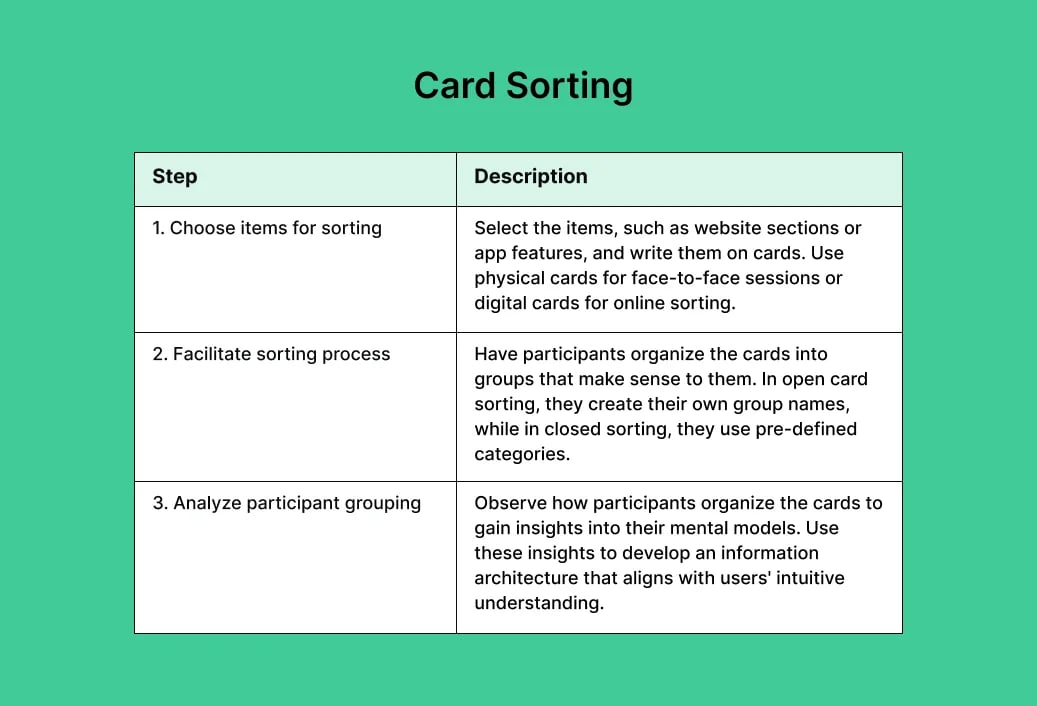
With card sorting usability tests, you can uncover missing or unnecessary features from users’ sorting activities and then use this data to optimize the whole navigation of your app to make it more user-friendly. It’s also a safeguarding way to make sure the designs match the developers’ original intention.
10. 5 Second Test
To collect users’ first impressions of a mobile app design and reaction, QA testers may consider using a 5 second test. 55% of visitors spend less than 15 seconds on a website, so grabbing someone’s attention in the first few seconds of them viewing a design is essential.
This test method helps you assess whether a mobile design can convey straightforward messages to its target audience. In the test, participants are shown an image of a landing page or screen for five seconds, and then the moderator will ask some follow-up questions for further data analysis.

Conclusion
Mobile usability testing is an integral part of your application development and management. According to Nielsen Norman Group, testing five people in one cycle reveals 85% of all usability issues. After a round, prioritize the problems and work on them, iterate, and test again. With continuous testing and optimizations, you’ll be able to deliver a highly-functional, user-friendly, and profitable app for your business.
How can Global App Testing help?
Global app testing can significantly aid in usability testing with diverse perspectives and insights from users worldwide. Here's how:
Using advanced targeting tools, obtain unmoderated feedback from a diverse pool of testers within 48 hours.
Moderated Usability Testing incorporating both client interviews and quantitative data analysis. This approach offers a balanced perspective on user experiences and their success in achieving set goals within the app.
Audit for design, localization, or functional errors to identify and address any errors or inconsistencies that may impact user experience.
Gain insights into user behavior and preferences across different regions and markets. Identify areas where users may be facing challenges, whether functional, user-related, or localization-specific and investigate underlying issues to improve overall usability and user satisfaction globally.
Interested in learning more?
Schedule a free demo of our platform today!
Keep learning
A guide to outsourced software testing
Software localization challenges and solutions[Guide]
11 Automation testing tools to consider
